-
General Article
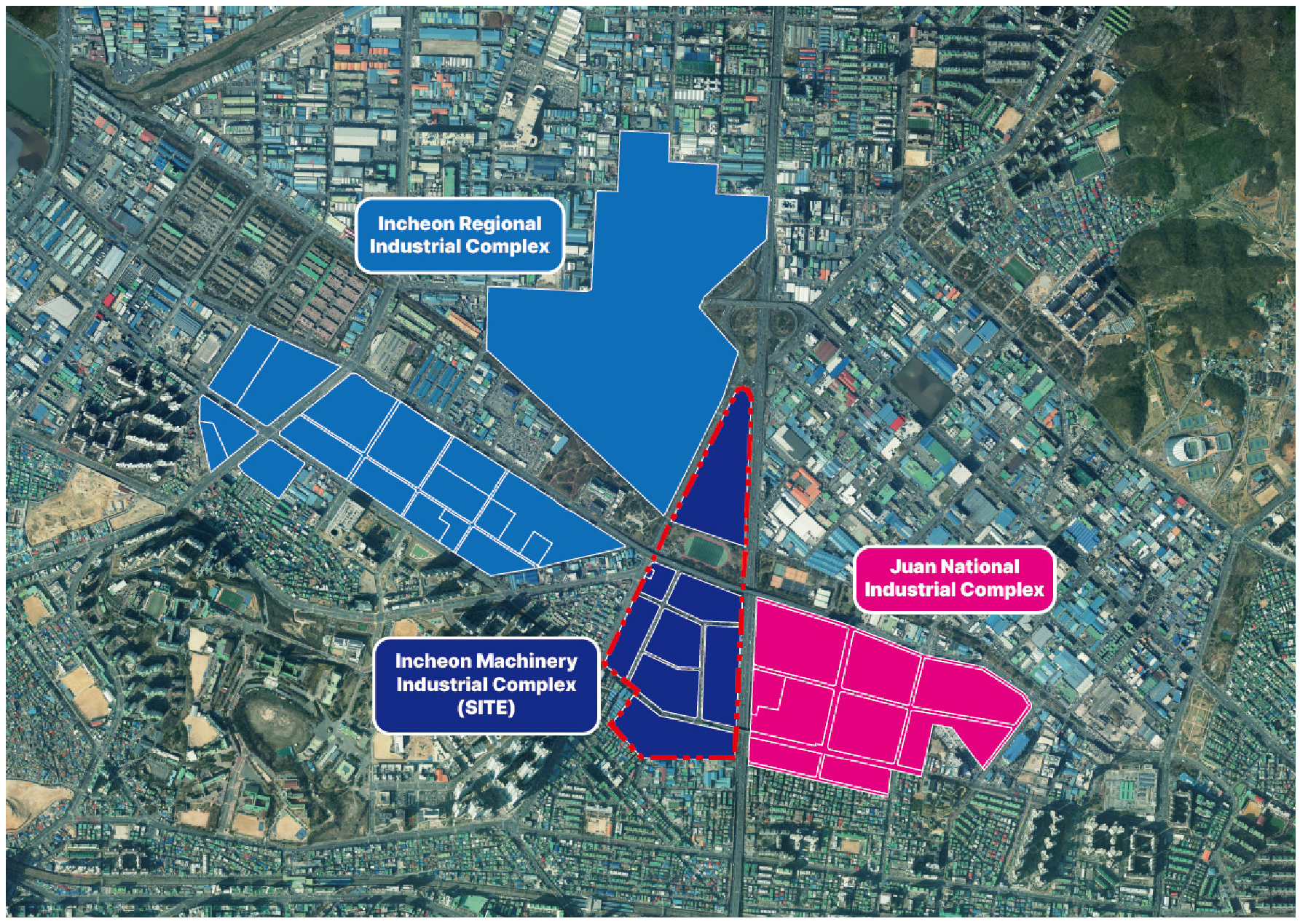
- A Study on site selection methods for regeneration anchor facilities in aging industrial complexes: Focusing on the incheon machinery industrial complex
- Taekyu Ha and Insu Na
- Since the 1960s, many industrial complexes established during Korea’s industrialization have deteriorated, not only in terms of production facilities such as factories …
- Since the 1960s, many industrial complexes established during Korea’s industrialization have deteriorated, not only in terms of production facilities such as factories but also in associated infrastructure such as roads, parks, and sewage systems. The deterioration and decline of these industrial complexes have become broader urban issues beyond localized problems, affecting industrial workers negatively and leading to material emissions, noise, traffic, nighttime hollowing-out, and spatial discontinuity. Traditional manufacturing-focused complexes from the past fail to meet modern demands influenced by technological advancements and heightened public awareness of industrial environments. To transform aging industrial complexes into advanced industrial zones, it is essential not only to improve physical conditions but also to consider environmental factors. Although many studies have been conducted on the structural advancement projects within redevelopment efforts, they mainly focus on urban planning aspects, necessitating research on spatial strategies at the architectural level. This study aims to derive candidate sites through a location feasibility analysis of regeneration anchor facilities within aging industrial complexes. These anchor facilities are envisioned to serve as catalytic nodes for environmental enhancement and industrial transformation, offering welfare and innovation services that can benefit both workers and surrounding communities. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
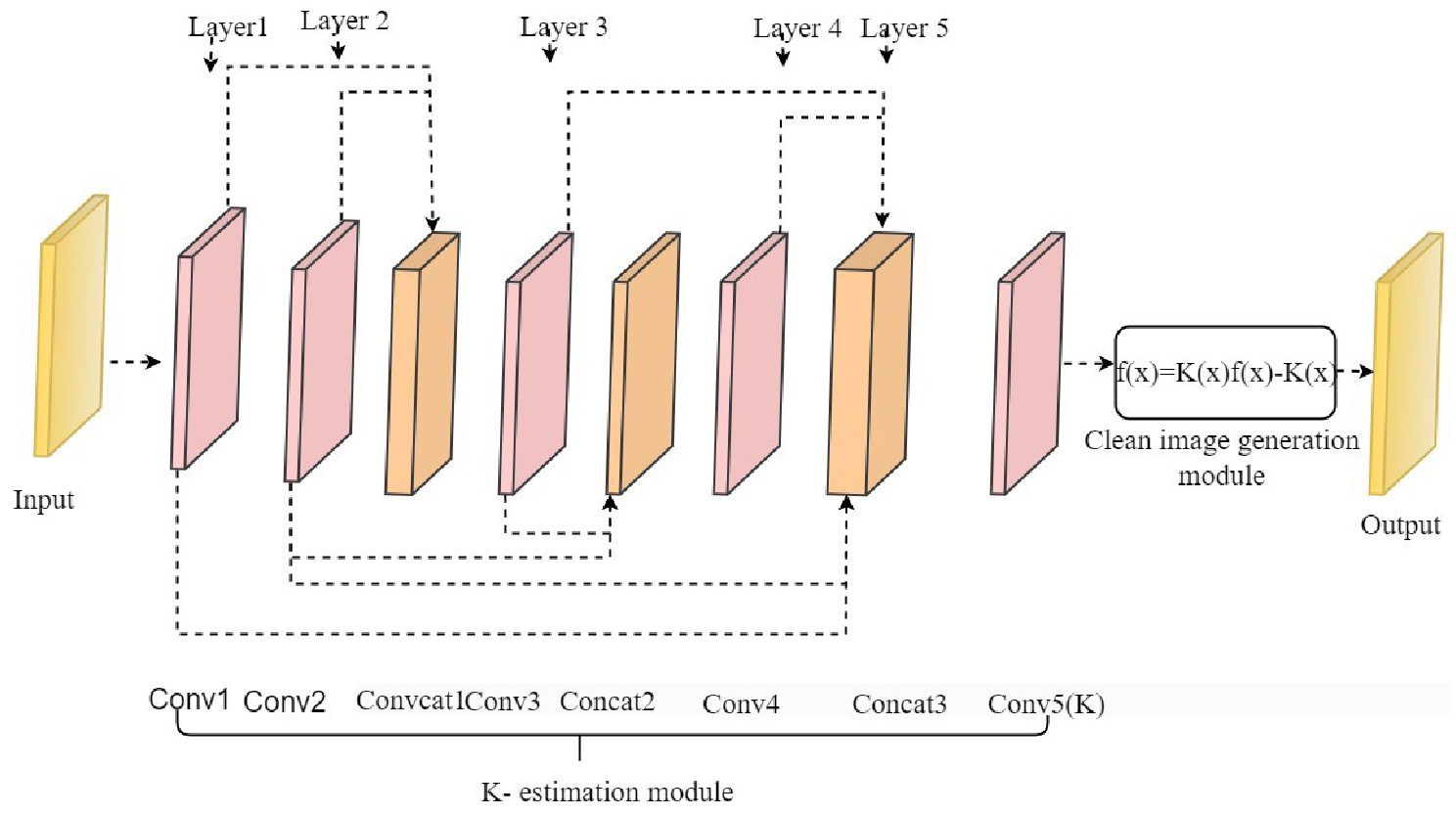
- Weather-aware deep learning framework for sustainable urban surveillance and infrastructure resilience
- Sandhya Sharma, Arjit Tomar and Pramod Kumar Sagar
- Extreme weather conditions such as fog, rain, snow, and sandstorms reduce visibility, hindering reliable monitoring of urban spaces and critical infrastructure. This …
- Extreme weather conditions such as fog, rain, snow, and sandstorms reduce visibility, hindering reliable monitoring of urban spaces and critical infrastructure. This limitation affects structural health inspections, facility management, and public safety, key components of sustainable urban development. This study introduces a weather-aware computer vision framework designed to maintain high detection accuracy under adverse meteorological conditions, supporting resilient and climate-adaptive urban monitoring. The system employs a modular two-stage deep learning pipeline, integrating weather-specific enhancement modules (AOD-Net for dehazing, DerainNet for deraining) into a learnable adaptive fusion network. Enhanced images are processed with Faster R-CNN for high- precision object detection. Evaluations on benchmark datasets (DAWN, MS COCO, EXDARK, PASCAL VOC) demonstrate superior performance over SSD, YOLOv3, and RetinaNet, achieving mAP@ [.5:.95] of 68.93 with F1-score 0.76, recall 0.73, precision 0.79, and IoU 0.64. Image quality metrics (SSIM = 0.89, PSNR = 27.93 dB, MSE = 101.37) confirm significant restoration capability. By ensuring accurate detection in challenging climates, the framework enables early hazard identification, improved asset management, and safer public spaces. Its scalability makes it suitable for smart city surveillance, autonomous inspection of building facades, and infrastructure resilience assessments. Future research will focus on lightweight deployment for real-time inference on edge devices, enabling cost- effective, energy-efficient, and sustainable monitoring solutions for weather-vulnerable urban environments. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
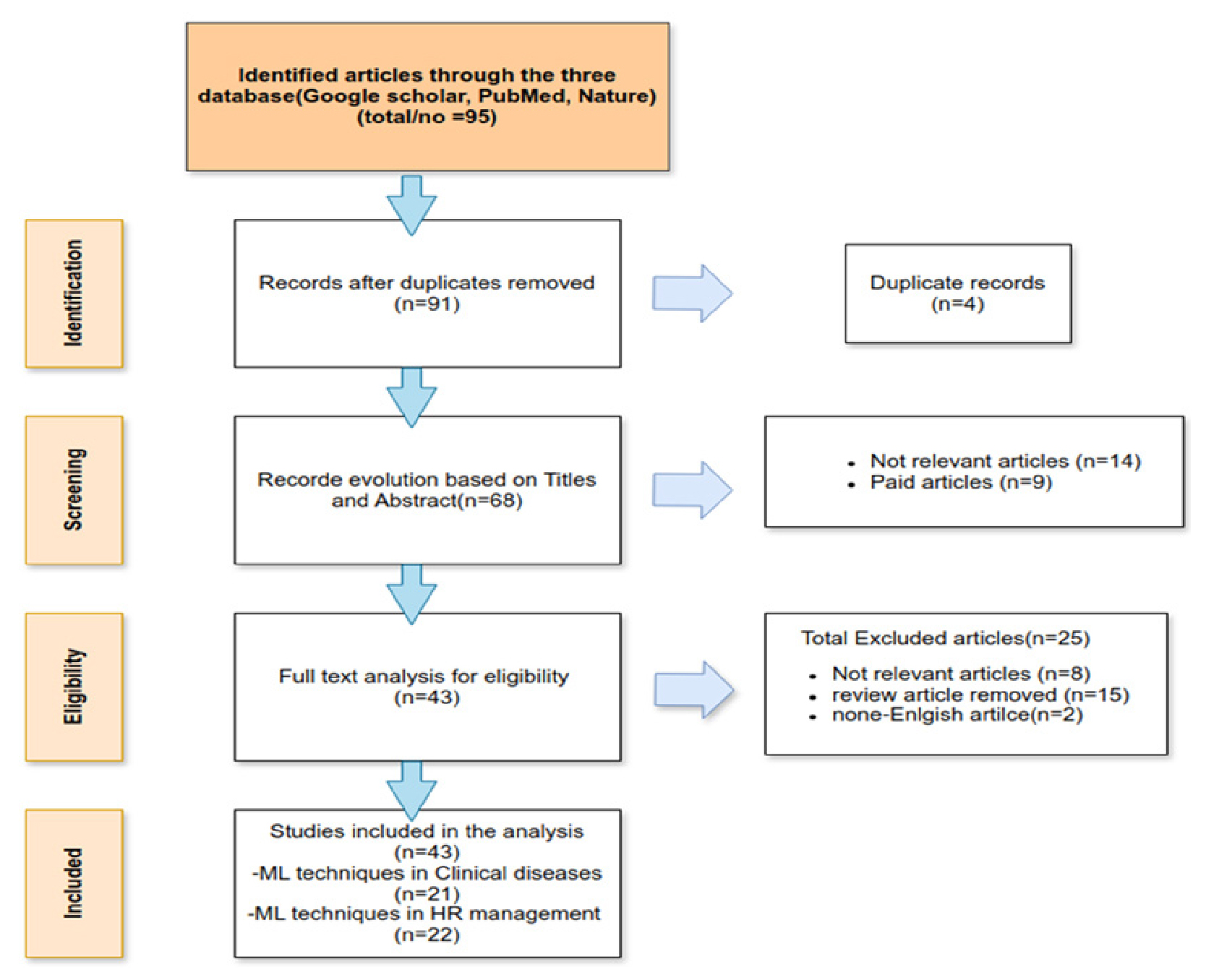
- AI-Driven approaches for sustainable urban development: A PRISMA systematic review of machine and deep learning applications in occupant health and facility management
- Abdullah Haidari, Nader Bahman, Nesar Ahmad Qauomi, Muktha Eti, Murari Devakannan Kamalesh, Pooja Sharma and Ankit Dilipkumar Oza
- Sustainable urban development relies on resilient health systems, healthy occupants, and efficient facility management. Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) provide …
- Sustainable urban development relies on resilient health systems, healthy occupants, and efficient facility management. Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) provide scalable decision- support tools that can strengthen these dimensions by transforming diverse health and environmental data into actionable insights. Using the PRISMA framework, this systematic review synthesizes ML/DL applications relevant to sustainable cities, with a focus on occupant health and healthcare workforce planning—two domains that directly influence sustainable building operations and urban resilience. We examine methods (tree-based models, CNN/RNN/LSTM, transformers) and data sources (EHRs, IoT and ambient sensors, wearables, environmental exposures, mobility, and administrative records) across tasks such as disease surveillance, risk stratification, bed-capacity forecasting, care-pathway optimization, and workforce scheduling. Reported deployments improve predictive accuracy, reduce wait times, optimize space and resource utilization, and enhance care coordination—contributing to healthier occupants and more sustainable healthcare facilities. However, challenges persist, including fragmented datasets, bias and fairness concerns, privacy governance, and limited reproducibility across urban contexts. To address these, we outline a practical workflow for operationalizing AI in sustainable healthcare and building environments: standards-based data integration (e.g., FHIR), transparent validation, MLOps pipelines, human-in-the-loop decision-making, and fairness auditing. By linking predictive modeling with occupant health monitoring and facility management strategies, this review provides a roadmap for integrating AI into healthcare-enabled sustainable building systems. Ultimately, leveraging ML/DL within urban healthcare infrastructure enhances resilience, efficiency, and well-being—key drivers for sustainable urban development and healthy building practices. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
- Frequency tunable terahertz antenna for structural health monitoring device and sustainable urban development
- Rahul Gupta, Hemlata Sinha, Anil Kumar Soni, Madan Pal Singh, Lohit Upadhyay and Deepika Bairagi
- The rapid advancement of smart and sustainable building technologies has created a growing need for compact, high-performance terahertz (THz) antennas to enable …
- The rapid advancement of smart and sustainable building technologies has created a growing need for compact, high-performance terahertz (THz) antennas to enable reliable indoor connectivity, non- invasive health monitoring, and advanced sensing of building environments. Conventional antenna design relies heavily on iterative electromagnetic simulations and manual tuning, which are resource-intensive and time-consuming, and often fail to capture the nonlinear parameter interactions important for structural and environmental applications. This paper introduces a two-stage hybrid machine learning framework that integrates MATLAB-based simulation-driven data generation with an Autoencoder-XGBoost pipeline to optimize frequency-tunable THz antennas for building-related sensing and communication tasks. The Autoencoder extracts critical latent features, while XGBoost accurately predicts key antenna performance metrics, such as return loss (S11), resonant frequency, bandwidth, and gain, which are defined earlier in the introduction to support interdisciplinary readers. In particular, the proposed antenna design enables low-power and efficient data transmission for structural health monitoring applications, such as temperature, humidity, and moisture sensing in building materials-facilitating early damage detection and improved energy management. The proposed hybrid approach significantly outperforms conventional methods (Random Forest, SVR, MLP), achieving near-perfect predictive accuracy (MSE = 0.001, RMSE = 0.03, MAE = 0.02, R2 = 0.99), with robust generalizability confirmed through error distribution and k-fold validation. Overall, the framework offers an effective, sustainable, and scalable solution for the design and optimization of THz antennas, supporting next-generation smart building monitoring, healthy indoor environments, and sustainable urban development applications. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
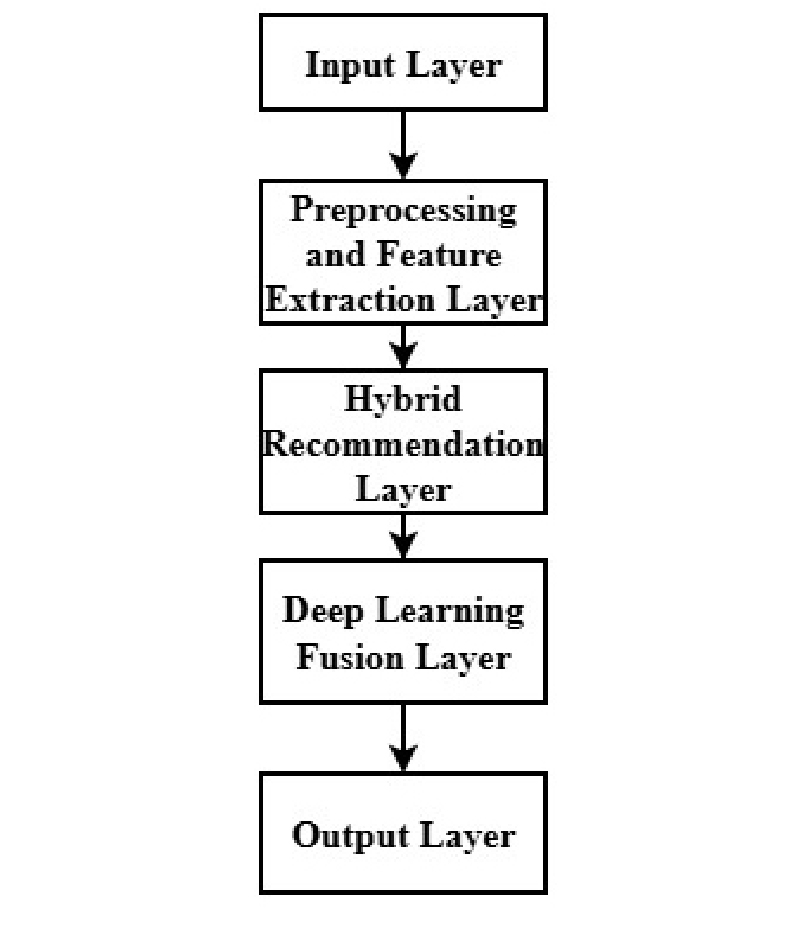
- A sentiment-aware hybrid deep learning framework for sustainable smart urban and social network ecosystems
- Shaifun Nahar Sonia, Rachita Kansal and Chander Diwaker
- This paper presents an emotion-sensitive hybrid deep-learning platform to facilitate smart city and social-networking implementations in order to achieve sustainability. The system …
- This paper presents an emotion-sensitive hybrid deep-learning platform to facilitate smart city and social-networking implementations in order to achieve sustainability. The system is a combination of Sentiment analysis (SA), Contend based filtering (CBF), and Collaboration filtering (CF) that provides context-based recommendations that increase user engagement and promotes sustainable digital interactions. BERT and RoBerta are used to classify emotions and combine the sentiment understanding with behavioral and content features to produce highly accurate and specific recommendations. This framework was tested using two real datasets, and the accuracy was 99.14%, which is better than other state of art methods. These findings indicate the role of sentiment sensitive Deep-Learning (DL) platforms in generating human-focused, intelligent and sustainable social- network ecosystems to enhance the objectives of smart urbanism. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
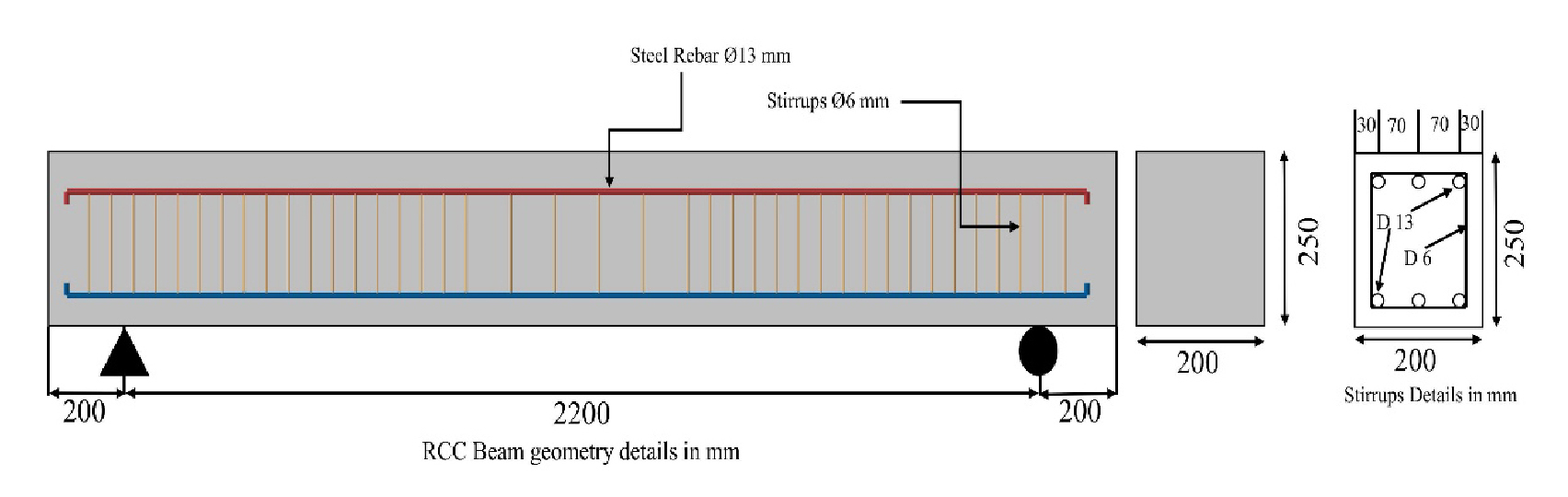
- Simulation of chloride diffusion and structural performance evaluation of sound and corroded RCC beams
- Prakhar Singh and Hanseung Lee
- This study describes the structural behavior of RC beams when subjected to different levels of corrosion by developing a finite element model, …
- This study describes the structural behavior of RC beams when subjected to different levels of corrosion by developing a finite element model, subsequently validating it with the help of experimental results. The analysis was run using ABAQUS to represent both the mechanical response as well as chloride diffusion within the beam. Validation data were adopted from earlier literature. The sound beam model has been validated first by comparing its load-deflection response against one derived from experiments with less than 5% deviation in ultimate load and very close agreement. The validated model was then used to simulate 10% and 20% corrosion levels, derived from the experimental corrosion equations, to assess the degradation in structural capacity. The result showed that the corrosion led to a clear deterioration of structural behavior, ultimate load decreased by approximately 17% for 10% and 33% for 20% corrosion, while peak bond stress from 7.2 MPa (sound beam) to 5.0 MPa and 2.5 MPa, respectively. A long term chloride diffusion analysis was performed to estimate the corrosion initiation, revealing that after 100 years of exposure the chloride ion reached the reinforcement depth, indicating a high probability of corrosion. The combined mechanical and diffusion analysis result demonstrate that corrosion significantly reduced stiffness, load carrying capacity, and bond resistance. Overall, the proposed FEM approach provides a reliable numerical framework for evaluating the mechanical performance and deterioration of RC beams affected by corrosion. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
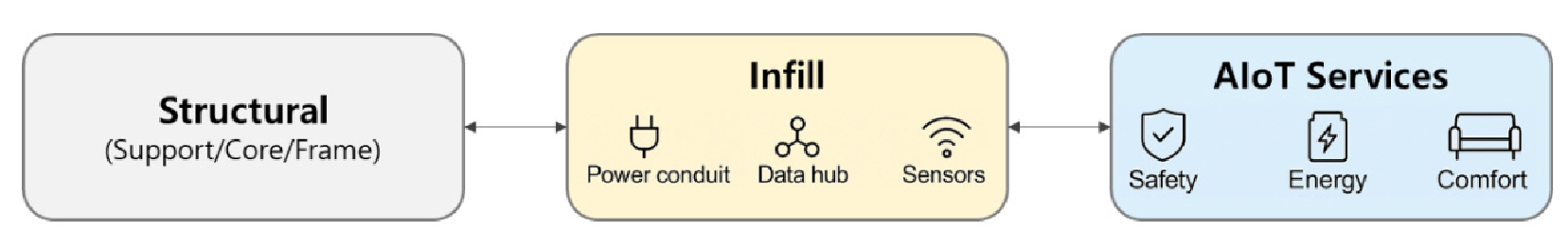
- A Study on proposing standardized AIoT installation guidelines for buildings based on analysis of IoT implementation building project
- Hyojin Lim and Chang-U Chae
- This study investigates the integration of AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things) devices into residential infill systems and proposes standardized construction guidelines based …
- This study investigates the integration of AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things) devices into residential infill systems and proposes standardized construction guidelines based on empirical analysis from a real-world smart housing testbed. Field observations revealed that sensors, smart lighting, wall pads, and gateways were primarily connected through embedded power and communication lines within ceiling, wall, and floor infill structures. However, inconsistencies in installation methods, non-standard wiring routes, and limited maintenance accessibility were frequently identified. To address these issues, this study derives key infill-level requirements—including wiring separation, installation clearances, inspection openings, and finish integration—and establishes installation criteria for major AIoT devices. International and domestic trends further confirm that infill systems form an essential physical foundation for AIoT-enabled smart housing. The findings demonstrate that AIoT devices must operate not as surface-mounted equipment but as embedded components integrated into infill layers to ensure stability, safety, and maintainability. The proposed guidelines provide empirical evidence that may support future incorporation of AIoT infill installation and maintainability criteria into national housing certification systems. Although based on a single testbed, this study establishes a new research direction in the standardization of AIoT–infill integration and offers a foundational model applicable to various building types to enhance the reliability and sustainability of smart housing. - COLLAPSE
-
General Article
- Advancing sustainable construction through BIM: Examining the link between barriers and benefits in prefabricated factory projects
- Ha Duy Khanh, Le Dinh Thuc and Huynh Trung Hieu
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a modern technological solution for designing and managing construction projects, widely adopted in many countries due to …
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a modern technological solution for designing and managing construction projects, widely adopted in many countries due to its numerous benefits. However, companies often face significant barriers when applying BIM, mainly due to varying conditions and capacities. This study aims to assess the importance of barriers in limiting the benefits of BIM during the pre-construction phase and to develop an evaluation model to analyze their relationship. Based on a review of the literature and expert surveys, the study identified 19 key benefits, grouped into five categories: enhanced visualization, cost reduction, time savings, efficient design, and improved collaboration. It also identified 11 significant barriers, categorized into three groups: human, facility, and process-related, within the Vietnamese construction industry. Data were collected through a structured questionnaire distributed to stakeholders with knowledge of BIM. The analysis revealed the most significant barriers related to low-quality human resources, high investment costs, and the absence of a legal framework for BIM implementation. In addition, the study found that these barriers have a relatively similar level of influence on BIM benefits. The study used multiple linear regression analysis to develop models to assess the impact of each barrier group on specific BIM benefits. The models demonstrated high accuracy and applicability, making them suitable for future forecasting. The findings can assist project stakeholders in developing more effective BIM implementation strategies by reducing barriers and maximizing benefits. - COLLAPSE
Journal Informaiton
 International Journal of Sustainable Building Technology and Urban Development
International Journal of Sustainable Building Technology and Urban Development
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 International Journal of Sustainable Building Technology and Urban Development
International Journal of Sustainable Building Technology and Urban Development













